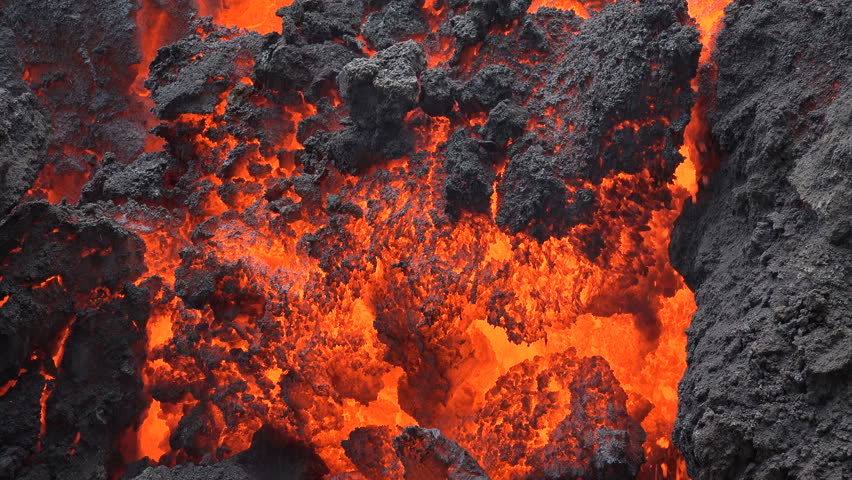


These can impact the climate and cause irritations, poisoning, breathing issues, and acidic rain. Gas eruptions escape through soil, lava, or vents and include gases such as carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, hydrogen, hydrogen sulphide, and carbon monoxide. Ash falls do not tend to endanger human life but can cause issues with aviation, infrastructure, and contamination to water and agriculture. Ash fallsĪsh falls are eruptions of ash clouds caused by the expansion of gas in the volcano. They can threaten nearby people and cause widespread death and destruction through burning. This means that they can travel a long way with little warning. They can travel at 80km/h, significantly faster than lava flows. Pyroclastic flows are eruptions of rock, ash, and gas that are superheated. The lava will destroy anything in its path by burning, burying, or knocking it down. However, these lava flows tend to travel slowly, which gives time for evacuation. Volcanoes can erupt with lava flow (molten rock) and damage nearby infrastructure. The harmful effects of volcanoes include lava flows, pyroclastic flows, ash falls, gas eruptions, and further secondary hazards. The volcanoes formed at the ocean-continent convergent plate margins are called Andean-type volcanoes. Volcanoes formed at the ocean-ocean convergent plate margins are called island-arc volcanoes. Let ’s see how different plate margins affect the magnitude and type of volcanic eruption.

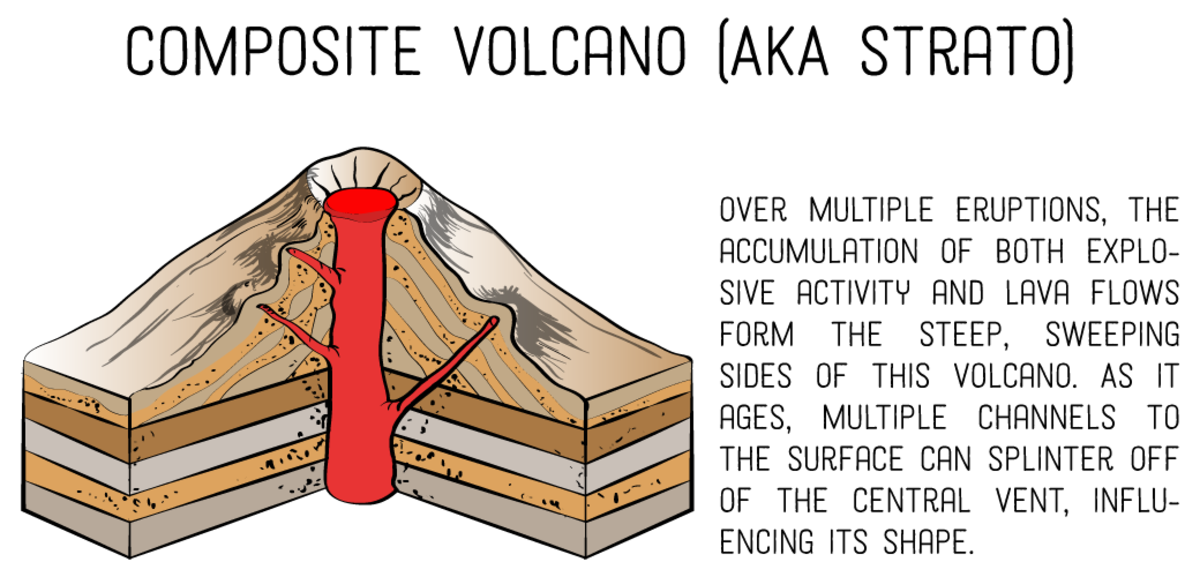
Mount Pelée, Martinique, lava dome, pixabay How do physical processes impact the magnitude and type of volcanic eruption? Lava domes are sometimes formed within the crater of a previous volcanic eruption. This process includes the outer surface hardening, breaking, and falling down the volcano ’s sides. The lava often remains around the vent, building the volcano from within. Lava domes are formed by lava that is too viscous to flow far. Shield volcanoes are more common in oceanic settings rather than continental.Įxample: Mauna Loa, Hawaii, is the world’s largest shield volcano. Basaltic lava pours out in different directions from the opening or a group of openings. Shield volcanoes consist mostly of fluid lava flow and are shaped (unsurprisingly!) like a shield. Mount Fuji, Japan, pixabay Shield volcanoes The cone is often destroyed when the volcano becomes inactive and hardened magma blocks the opening. They are often steep-sided and have symmetrical cones. Parícutin volcano, Mexico, Jim Luhr, Smithsonian Institution, Public Domain Composite volcanoesĬomposite volcanoes are formed by alternating layers of lava, volcanic ash, cinders, blocks, and bombs. This cinder falls around the opening and forms a circular or oval cone.Įxample: The Parícutin volcano in Mexico. When the gaseous lava is ejected into the air, small fragments solidify and form cinder. Cinder conesĬinder cones are formed by the particles from lava that erupt from a single opening. The different types of volcanoes include cinder cones, composite volcanoes, shield volcanoes, and lava domes. What are the different types of volcanoes?

Extinct volcanos will never erupt again and are no longer a danger.Dormant volcanoes are those that have not erupted for over 2000 years.This means that they have erupted or could still erupt.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
